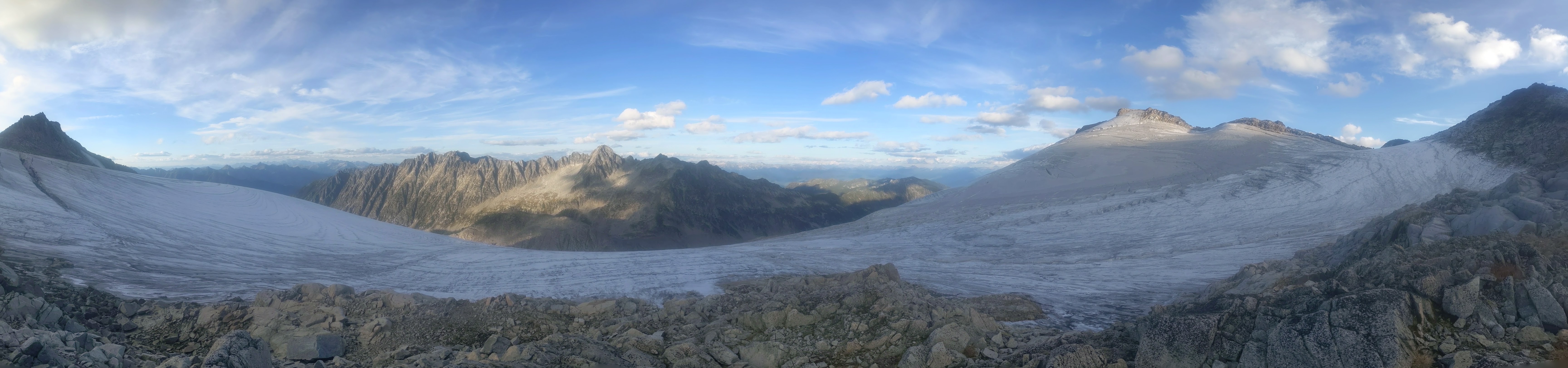
The panorama above The southwest side of Kokanee Glacier from the ridge with Cond Peak at the Right and Sawtooth Ridge at center.
By Ben Pelto, PhD, UBC Mitacs Elevate Postdoctoral Research Fellow
Since 2013 I have been working on the Kokanee Glacier. Located just outside of Nelson in southeastern British Columbia (BC), the Kokanee Glacier is due north of the Washington-Idaho border. This work began as part of a five-year study of the cryosphere in the Canadian portion of the Columbia River. This project was carried out by the Canadian Columbia River Snow and Glacier Research Network – spearheaded by the Columbia Basin Trust. The glacier research, which included the Kokanee Glacier, was led by my former PhD supervisor at the University of Northern British Columbia Dr. Brian Menounos and myself. At the culmination of the project, we published a technical report, and a plain language summary of that report. When the five-year project officially ended in 2018, I learned of a BC Parks program called Living Labs, which offers funding for climate change research in BC Parks, particularly research which documents change and guides protected area management. With Living Labs funding in 2019-2021, I have kept the annual mass balance trips going – now a continuous nine-year record – and a winter mass balance trip in 2021. In conjunction with this, Brian Menounos has secured continued funding (continued from our 5-year project) from BC Hydro for LiDAR surveys of the glacier every spring and fall. These surveys are carried out by the Airborne Coastal Observatory team from the Hakai Institute.
During the 2021 spring trip, we found that the Kokanee Glacier had an average snow depth of 4.4 meters. Using snow density measurements collected with a snow-corer, we found that the winter balance for 2021 was 1.91 meters water equivalent (m w.e.). This value was lower than the 2013-2020 average of 2.18 m w.e. (Pelto et al. 2019).
-
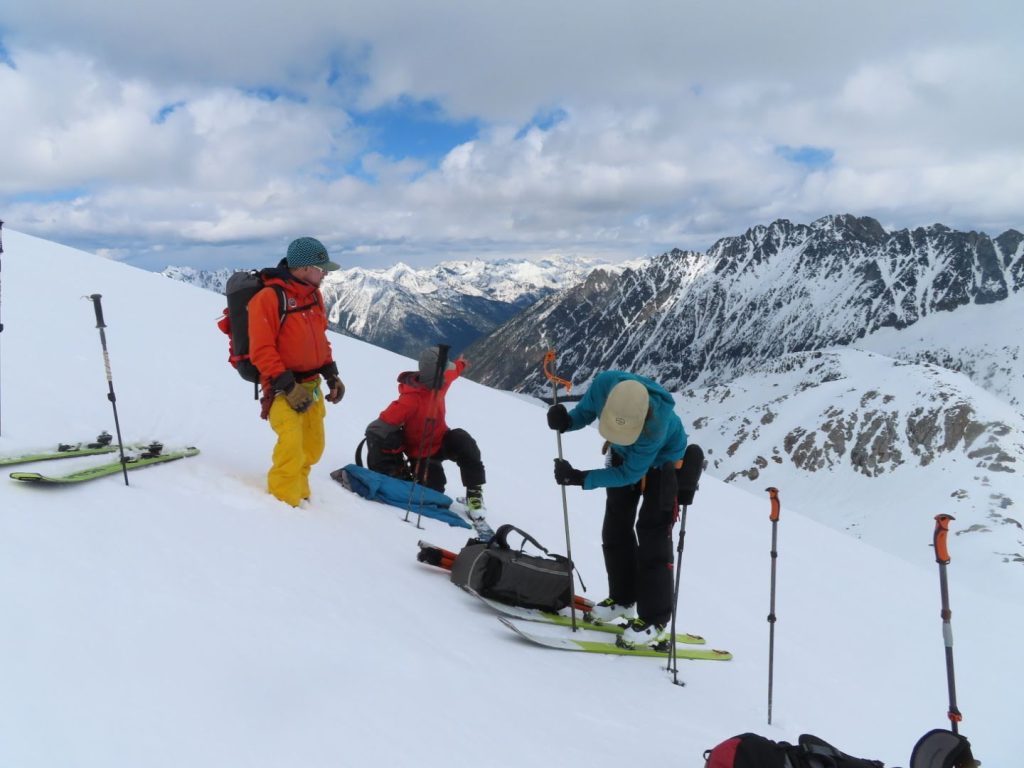

Ali Schroeder probing snow depth on the Kokanee Glacier while Joel McBurney and Drew Copeland look on. -
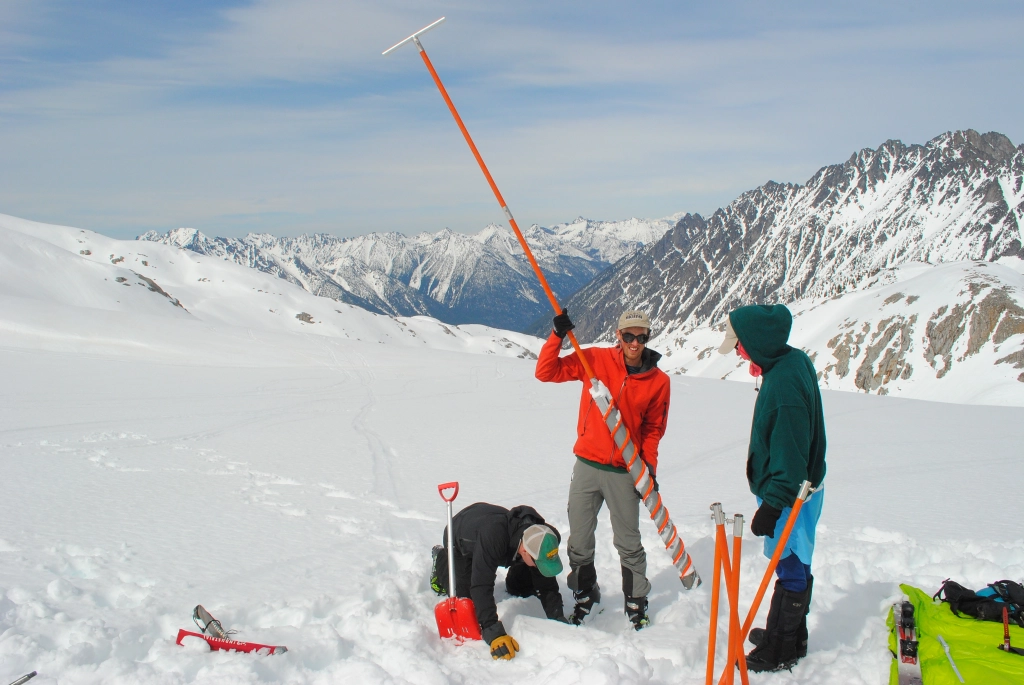

Ben Pelto with the snow corer with Tom Hammond and Micah May on Kokanee Glacier. Photo: Jill Pelto
With a below average winter balance, 2021 would need to feature a cool summer. Instead, multiple heat waves occured, with temperature records being broken across the province. Wildfires burned all over BC and the neighboring US states of Washington and Idaho, swamping the region in smoke for weeks on end. Rather than mitigate for a slightly-below-normal snowpack on the Kokanee, summer 2021 took a blow-torch to glaciers across the region.
We hiked into the Kokanee Glacier on September 12, stopping under a boulder to wait out proximal booms of thunder and flashes in the clouds. We got pelted with bursts of both hail and graupel, and soaked in the rain, before gingerly working our way up boulder field and talus that is climbers route up the Keyhole to the Kokanee Glacier. Like the satellite imagery had shown, there was no snow in sight on the glacier – bare ice only. Instead of my usual camp on the snow, we chose a climbers bivy site to set our tent.
Stepping out onto the glacier, we immediately ran into difficult terrain, crevasse bridges of snow or firn had collapsed, leaving bedroom-width crevasses gaping open, necessitating an exercise in maze navigation. Our first stop was a stake at 2600 m which typically retains snow (50 to 100 cms), but this year had lost 1.6 meters. In fact, two stakes drilled at the site in 2015 and subsequently buried by snow had melted out, demonstrating that all snow/firn from the intervening years had been lost. This observation clued me in to the magnitude of melt to expect this year.
Travel on the glacier was more challenging in spots, but overall faster, as the total lack of snow meant that most crevasse bridges were gone, requiring less probing of crevasse bridges and roped-travel. Later, using a satellite image from the dates of our visit, I mapped the retained snow cover, limited to two tiny patches high on the glacier’s east side. The accumulation area ratio (AAR), or the ratio of snow cover to bare ice/firn was <0.01, meaning that under 1% of the glacier was covered in snow.
-

The upper reaches of Kokanee Glacier to Cond Peak (2800 m) with no retained snow in 2021. Bare ice is exposed on the lower half of the image, and firn, or multi-year snow above -

The brown surface is multi-year firn, exposed by the loss of snow. In a typical year, the snow line would be visible here. The white surface below the brown is bare glacier ice.
 Near infrared-Red-Green 30 cm resolution ortho image of Kokanee Glacier from the Hakai Geospatial/ACO team on Sept. 2, 2021. Note how badly crevassed the glacier is, most crevasses are exposed with no retained snow. The white color and mottled appearance over the upper glacier is a skiff of overnight snow just a few centimeters thick that melted off the next day. Also note bare ice patches exposed under formerly perennial snow patches that have shrunk in recent years and now are disappearing.[/caption]
Near infrared-Red-Green 30 cm resolution ortho image of Kokanee Glacier from the Hakai Geospatial/ACO team on Sept. 2, 2021. Note how badly crevassed the glacier is, most crevasses are exposed with no retained snow. The white color and mottled appearance over the upper glacier is a skiff of overnight snow just a few centimeters thick that melted off the next day. Also note bare ice patches exposed under formerly perennial snow patches that have shrunk in recent years and now are disappearing.[/caption]
Visiting the toe of the glacier, our lowest stake indicated just under 5 m of ice melt, double that of 2020. In May, this location had 3 m of snow; the combined melt of snow and ice (loss of winter snow and glacier ice) is termed the summer mass balance, and at this site was -6.2 m w.e., far higher than the usual -4 m w.e. I also noticed that much of the thin ice along the margin of the toe was gone, and a little rock nunatak (rock island) that appeared in 2015 (images below) became a bite out of the glacier rather than a island. We estimated that the toe experienced 60 m of retreat. Over the past 5 years, the Kokanee has lost an average of 16 m in length annually. Expecting to see above average thinning and retreat, I was still startled to see how diminished and thin the toe looked.
A week prior to my field visit, the Hakai Institute ACO team flew a LiDAR survey of the Kokanee Glacier as part of their work with Brian Menounos at UNBC. Comparing this year’s glacier surface with that from last year’s survey, Brian found a whopping 2.55 m of thinning. After mapping the glacier facies (ice/firn/snow) to represent on the density of the observed thinning, this equates to a glacier mass balance of -2.16 m w.e., higher than the previous record loss of -1.20 m w.e. in 2015.
 LiDAR-derived height change 2020 to 2021 from 1 m resolution DEMs from Brian Menounos and the Hakai Institue ACO team. The black line is the 2021 glacier outline, note the bite out of the glacier above the toe to the NE corner of the glacier. Small red patches off-ice are seasonal snow patches losing mass. Points represent mass balance observation locations.
LiDAR-derived height change 2020 to 2021 from 1 m resolution DEMs from Brian Menounos and the Hakai Institue ACO team. The black line is the 2021 glacier outline, note the bite out of the glacier above the toe to the NE corner of the glacier. Small red patches off-ice are seasonal snow patches losing mass. Points represent mass balance observation locations.
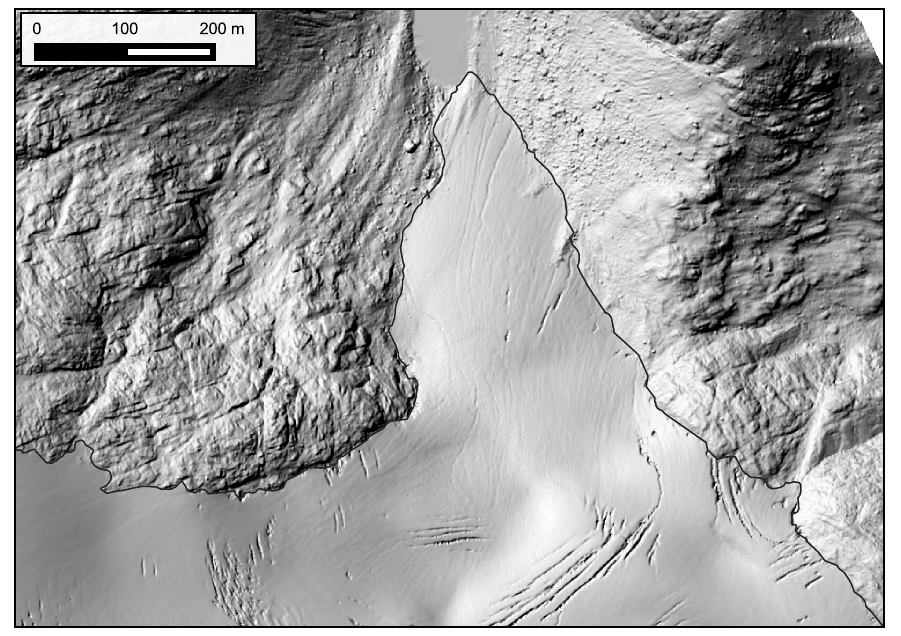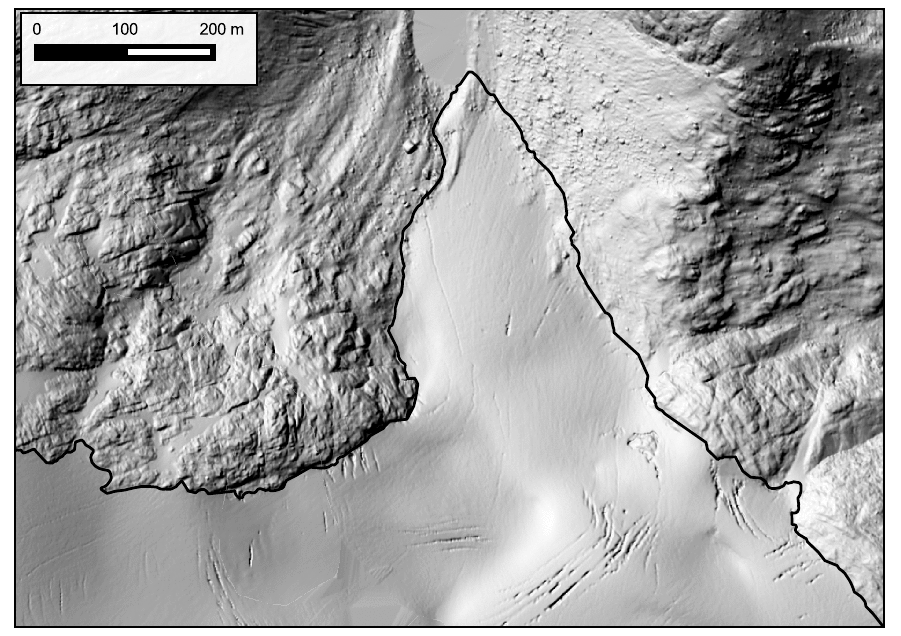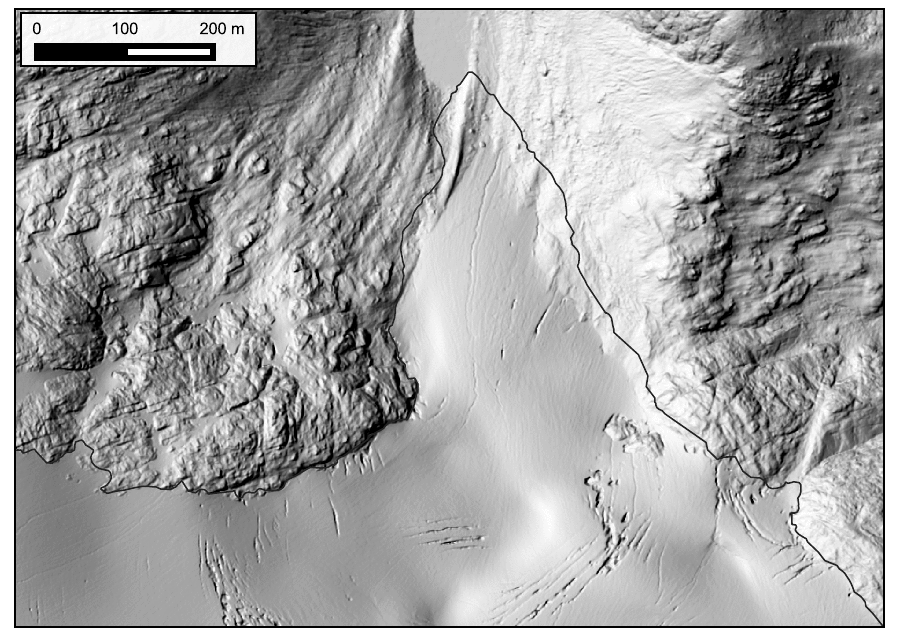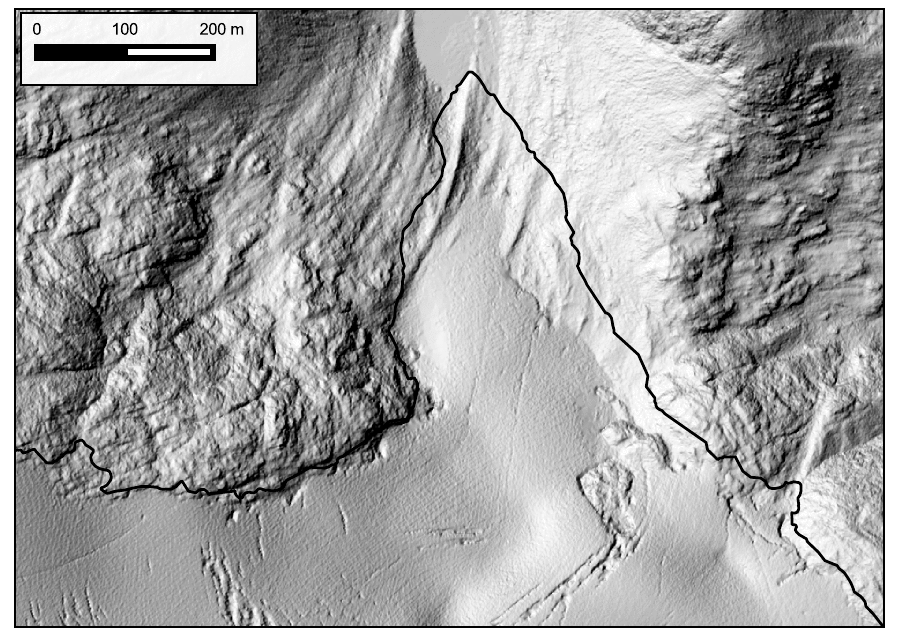 Kokanee Glacier terminus from 2015 to 2021. 140 meters of retreat for 23 m/yr. Data in the GIF are from Hakai Institute and Brian Menounos of UNBC ACO glacier surveys.
Kokanee Glacier terminus from 2015 to 2021. 140 meters of retreat for 23 m/yr. Data in the GIF are from Hakai Institute and Brian Menounos of UNBC ACO glacier surveys.
Back home, I crunched the numbers from our glaciological observations of mass balance (consisting of 14 ablation stakes this year) and calculated a mass balance of -1.97 m w.e. With Brian, I published a paper in 2019 (Pelto et al. 2019) comparing glaciological (field) and geodetic (LiDAR) mass balance estimates and found them to be similar – if some factors like snow and firn density were carefully considered. The small difference between estimates is likely due to timing (the LiDAR mass balance is from 8/26/2020 to 9/3/2021, while the field mass balance is 9/12/2020 to 9/13/2021), and that there was a skiff of fresh snow (likely 5-10 cms) on the glacier during the 2020 LiDAR survey.
 Kokanee 2021 glacier mass balance. Blue dots are observations. The boxplots show the 100 m bins used to estimate glacier-wide mass balance (median line in black, mean dashed grey line). The grey bars depict the area of the glacier for each 100 m elevation-band.
Kokanee 2021 glacier mass balance. Blue dots are observations. The boxplots show the 100 m bins used to estimate glacier-wide mass balance (median line in black, mean dashed grey line). The grey bars depict the area of the glacier for each 100 m elevation-band.
 Seasonal and annual mass balance for Kokanee Glacier from LiDAR and glaciological measurements for each balance year from 2013 to 2021 with 2σ uncertainties.
Seasonal and annual mass balance for Kokanee Glacier from LiDAR and glaciological measurements for each balance year from 2013 to 2021 with 2σ uncertainties.
In 2017, I visited the Kokanee Glacier to measure it’s ice thickness using ice-penetrating radar. I found that the glacier on average was 43 m thick using my measurements to tune a glacier model. I published these results in the Journal of Glaciology (Pelto et al. 2020). In the five years since that work, the glacier has lost over 4.8 m of total thickness. That equates to a loss of over 11% of its total volume. 2021 alone wasted away 6% of the glacier’s total volume — an eye-watering number for a single year.
 Cumulative mass balance for Kokanee Glacier 2013-2021 from both field and LiDAR measurments. LiDAR-derived mass balance began in 2016.
Cumulative mass balance for Kokanee Glacier 2013-2021 from both field and LiDAR measurments. LiDAR-derived mass balance began in 2016.
The heat of 2021 was an outlier, but years like 2021 and 2015 take a toll on the glaciers. Currently, glaciers in western North America are losing around 0.75 m of thickness per year (according to my work in the Columbia Basin (Pelto et al. 2019) and work by Brian Menounos for all of western North America (Menounos et al. 2018)). The better years for Kokanee Glacier (2016 mass balance: +0.12 m w.e.) pale in comparison. That meager surplus was lost the very next year (2017).
Herein lies the issue, positive mass balance years in recent decades are not large enough to offset even average years; hot dry summers take years off the lifespan of glaciers across western North America.
Losing 6% of it’s total volume in 2021, the best we can hope for Kokanee Glacier is a few near-neutral or positive mass balance years to cover back up the exposed firn, to keep the glacier albedo from becoming too dark and increasing the rate at which ice can melt.







